Introduction
In the world of automotive manufacturing, rubber seals play a quiet but indispensable role. They prevent leaks, block contaminants, withstand extreme temperatures, and ensure long-term reliability of highly complex machinery. Although they seem far removed from the day-to-day operation of healthcare facilities, automotive rubber seals offer a surprisingly relevant lens through which to understand durability, hygiene, safety, and preventive maintenance – core pillars shared by both industries. By exploring how these components function and why they matter, healthcare professionals can gain insights into material selection, equipment longevity, environmental control, and operational efficiency.
Definition
Automotive rubber seals are flexible, durable components used throughout a vehicle to prevent the entry of water, air, dust, and noise into critical areas such as doors, windows, the trunk, and the engine compartment. Made from materials like EPDM or silicone, they ensure proper insulation, reduce vibration, and protect internal components from environmental damage, contributing to overall vehicle comfort, performance, and longevity.
What Are Automotive Rubber Seals?
Automotive rubber seals are specialized components used throughout vehicles to protect internal systems from environmental exposure. They are found in doors, windows, engines, transmissions, fuel systems, HVAC units, and electrical housings. Their primary functions include:
- Creating airtight and watertight barriers
- Absorbing vibration and reducing noise
- Withstanding extreme temperatures and chemical exposure
- Enhancing performance and longevity of mechanical systems
These seals can be made from various elastomeric materials, such as EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer), silicone, nitrile rubber (NBR), fluorocarbon (like Viton®), and natural rubber blends. Each material is selected for its compatibility with environmental conditions—just as healthcare equipment relies on materials resistant to microbes, cleaning agents, and frequent sterilization.
Why They Matter: Reliability Through Material Science
One standout characteristic of automotive rubber seals is their ability to perform consistently under high stress. Modern vehicles endure:
- Constant mechanical movement
- Temperature fluctuations from below freezing to over 200°C
- Exposure to oils, coolants, fuels, dust, and moisture
- Repeated pressure and vibration
To achieve longevity, engineers rely not only on rubber’s natural elasticity but also on precise formulations, reinforcements, and design geometries that optimize sealing performance.
In healthcare settings, similar factors drive material selection for gloves, gaskets in diagnostic devices, tubing, sterilization equipment, and medical-grade seals. While the environments differ, the underlying engineering principles – chemical resistance, flexibility, tear strength, and hygienic performance – are remarkably aligned.
EPDM: The Standout Material Shared Across Industries
EPDM rubber is a prime example of cross-industry relevance. It is used extensively in cars for door seals, window channels, and weatherstripping because of its:
- Resistance to UV radiation
- Excellent performance in extreme temperatures
- Long life and low maintenance
- Resistance to ozone, steam, and mild chemicals
Healthcare facilities also rely on EPDM in HVAC gaskets, steam sterilizer seals, anesthesia machines, water purification systems, and facility plumbing. Its durability helps maintain environmental control – something essential for infection prevention and patient comfort.
Environmental Control: A Shared Priority with Healthcare Facilities
One of the most overlooked similarities between automotive sealing systems and healthcare infrastructure is the importance of controlling environmental exposure. In vehicles, seals maintain interior comfort, protect engine mechanisms, and ensure the safe function of electronic components. Without them, humidity, particulate matter, and temperature shifts could compromise performance.
Healthcare facilities face an even higher standard. Operating rooms, isolation rooms, laboratories, pharmacies, and imaging suites require tightly managed air pressure and humidity levels to keep patients safe and support sensitive equipment. Many of these systems rely on precision sealing components similar in function to automotive rubber seals. For example:
- Door gaskets in sterile environments help maintain positive or negative pressure.
- Medical HVAC systems depend on durable elastomeric seals to prevent air leakage.
- Refrigerated medication storage uses rubber sealing technologies to maintain consistent temperatures.
The concept is the same: sealing integrity directly affects safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
Preventive Maintenance: Lessons from the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry places enormous emphasis on preventive maintenance. Rubber seals are regularly inspected because:
- A small leak can escalate into major mechanical failure.
- Degraded seals lead to inefficiency and costly repairs.
- Environmental exposure gradually weakens elastomeric materials.
Healthcare facilities benefit from adopting a similar mentality. Many system failures—HVAC malfunctions, imaging equipment downtime, sterilizer issues, or even plumbing leaks—can be traced back to aging or compromised sealing components.
Key practices healthcare operators can borrow include:
- Routine inspection schedules for all elastomeric components
- Using manufacturer-recommended replacement intervals
- Monitoring temperature, chemical exposure, and pressure changes
- Documenting wear patterns to improve maintenance planning
Proactive attention to seals can significantly reduce downtime, maintenance costs, and risks of contamination.
Hygiene and Sterility: When Rubber Meets Healthcare Standards
While automotive seals are designed to resist dirt, contaminants, and chemical exposure, healthcare environments introduce stricter hygiene requirements. Medical sealing materials must be:
- Non-porous
- Resistant to microbial contamination
- Able to withstand repeated cleaning and sterilization cycles
- Compatible with disinfectants, alcohols, and chlorine-based agents
This makes silicone rubber, fluorocarbon rubber, and certain EPDM blends ideal for applications like surgical tools, medication delivery systems, dialysis equipment, and lab instruments. Though automotive seals do not require sterility, the material engineering behind them – especially the focus on longevity and environmental resistance – mirrors the engineering demands of the healthcare sector.
Noise Reduction and Patient Comfort
Automotive seals also serve a secondary purpose: noise and vibration reduction. Door seals, window channels, and engine compartment gaskets all contribute to quieter cabin environments.
In healthcare spaces, acoustic comfort plays a vital role in:
- Patient recovery
- Sleep quality in inpatient rooms
- Stress reduction for staff
- Privacy and confidentiality
Rubber-based sealing solutions in doors, windows, ventilation systems, and movable partitions help reduce sound transmission and create quieter clinical environments. Hospitals adopting modern noise-control designs often use elastomeric sealing technologies inspired by automotive engineering.
Sustainability and Recycling of Rubber Components
Sustainability is increasingly important in both automotive and healthcare industries. Automotive manufacturers are working to recycle more rubber and create closed-loop systems that reduce environmental impact. Advances include:
- Reclaimed rubber blends
- Bio-based elastomers
- Lower-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations
- Improved manufacturing processes that reduce waste
Healthcare facilities can adapt similar sustainability measures, especially in non-critical elastomeric components used in infrastructure or equipment. As material science progresses, recycled or bio-based rubber may become more common in medical-grade applications as well.
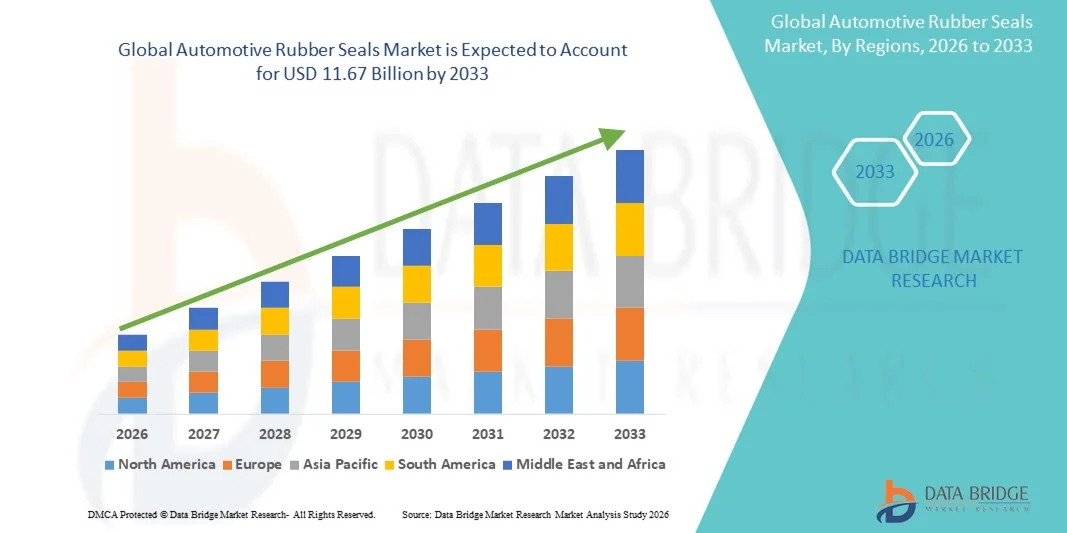
Growth Rate of Automotive Rubber Seals Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the automotive rubber seals market was estimated to be worth USD 8.57 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.93% to reach USD 11.67 billion by 2033.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-automotive-rubber-seals-market
Conclusion
Automotive rubber seals may seem like highly specialized components belonging strictly to vehicle manufacturing, but their principles, materials, and engineering insights hold significant value for healthcare environments. From environmental control and infection prevention to equipment maintenance, acoustic comfort, and sustainability, the performance characteristics of automotive seals mirror many of the demands found in medical settings.